In this age of digitalization, video content is trending on every online platform. Whether it is marketing specialists, media production professionals, or content creators, all noticed a prominent surge in video demand this year.
However, handling these huge files is not that simple anymore due to the exponential growth in their size. Uploading or sending these files online or other systems has become a challenge for users.
If you are tired of waiting for your large video file transmission, you need to stick to this guide as we go over the best way to send large video files. Here, we will discuss the 6 ways to transfer large video files. Let’s get started!
Part 1: Why Is Video File Transmission Important?
We are living in the age of video content hype. There is an increased demand in the film and television industry due to the rapid growth of online streaming platforms and social media videos. Netflix, YouTube, TikTok, and similar others are just examples that are making video content overtake traditional search engines.
Interestingly, the video shares on social media score 1200% more than text and image content combined, which speaks about the potential. So, the increased demand for video content is thereby increasing the demand for video production. This means that there is a growing need for video file transmission, as it is essential to ensure collaboration among video producers, editors, and distributors.
Part 2. 6 Ways to Transfer Video
There are many ways to transfer and send large video files. So, we have compiled 6 popular ways to send big video files, as follows:
Way 1: UDP-based File Transfer
UDP-based file transfer is one of the fastest ways of sending video files. This solution works with User Datagram Protocol, which is a connectionless file protocol ensuring direct and high-speed file transmission.
Organizations prefer UDP-based file transfer to send large files reliably and quickly, especially media files like videos. Aspera, File Catalyst, and Signiant are popular UDP-based file transfer providers. These solutions offer reliable features like pause/resume or auto-retry functionality. However, they are quite expensive.
Way 2: FTP servers
If you want to try an in-house and old-school file transfer method, you can go for FTP servers. Dating back to 4 decades, an FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is used for transferring files in organizations. It was particularly designed for transmitting large files online.
Using this method, you don’t send the files directly to the recipient. Rather, they are sent to a central server, which acts as the storage unit and handles all uploads and downloads. Without any size restrictions on single transfers, you can transfer multiple files simultaneously or schedule future transfers. Some free FTP clients include FileZilla and Xlight. However, FTP servers are not completely secure.
Way 3: Cloud Storage Solutions
Another best way to send videos is cloud storage solutions. They are great to upload video file to share or store. Google Drive, Dropbox, and OneDrive are giant cloud service providers that offer click-based interface, free cloud storage, and a seamless way to send large video files.
These solutions support most file formats and are easily accessible. Moreover, these tools are cost-effective and don’t cost you hefty amounts for extra storage. For instance, Google Drive offers free storage for your first 15 GB of space and is undoubtedly the best way to send video online.
Way 4: Shipping Hard Disk or USB Flash Drive
If you or your recipient is experiencing limited internet bandwidth, you can ship a hard disk or USB flash drive through a local courier service or international shipping provider like FedEx.
Hard disk and USB flash drives are great for transferring media files to your friends or coworkers manually. This helps secure the content from online theft, but it is time-consuming and less efficient than other advanced options.
Way 5: Compression and ZIP
Another effective method to send large video files is to compress and reduce their size. In this way, the files require less space to be transferred.
The best thing is that the ZIP option is available on every computer (OS). You only need to right-click the folder and tap “Compress to ZIP file”. Once done, your file is ready to be sent. You can try some free compression tools like WinZip, 7-Zip, and Express Zip.
Way 6: Raysync

Raysync is the most advanced, robust, and high-speed large file transfer solution method. It offers 100 times faster speed than FTP/HTTP with unlimited transfer volume for any video file size. Its cutting-edge technology enables smooth transfers of bulky files over long distances regardless of network conditions.
Some of the key reasons that make Raysync stand apart in the industry are:
- 100 Gbps bandwidth
- High-speed petabyte-scale large file transfer
- Flexible and easy to integrate
- Support data transfer across platforms (Windows, macOS, Linux), devices, networks, and storage (local, cloud, SMB, NAS, etc.)
- AES-256 and TLS encryption for high-end security for safe video file transmission
- Auto files sync & data backup
- Intelligent management dashboard
In short, Raysync’s advanced file transfer capabilities make it best to send long videos through an encrypted and reliable channel.
Part 3: Raysync vs. Other Transfer Methods – Advantages and Disadvantages
Raysync is an advanced solution for handling large file transfers effectively. Other than being a smooth and seamless way to send large video files, it has an edge over other methods with exceptionally fast speed, a military-grade encrypted framework, and super simple integration.
Below are the key advantages and disadvantages of Raysync vs. other transfer methods:
Advantages:
- Super-fast speed (100x faster speed than FTP/HTTP)
- Multi-OS support
- Peer to Peer transfers
- Unidirectional and bidirectional sync transfers
- Easy and simple installation
- Cost-effective solution
- User-friendly interface
- Unlimited transfer volume
- AES-256 and TLS encryption for high-end security
- Antivirus functionality
- Responsive technical support team
- Intelligent management dashboard
Disadvantages:
- Limited language support
Part 4: How to use Raysync to transfer large files?
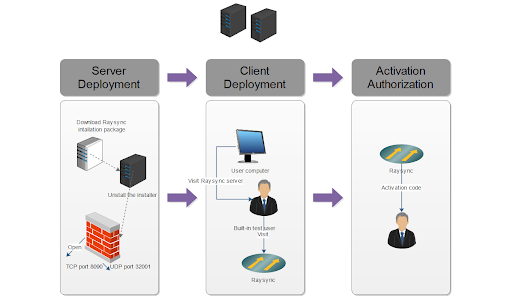
Now that we know the capabilities of Raysync in efficient and super-fast large file transfer, let’s quickly look at the steps to use Raysync to transfer large files:
First step:
Server Deployment: First, you need to have a machine that will serve as your server. Download the Raysync Transfer package and unpack and start it on your server. Then, open TCP ports 8090, 9090 and UDP port 32001 on your firewall to ensure smooth data transmission.
Second step:
Client Deployment: Transfer users can visit the webpage of Raysync client at http://ip:8090, download and install Raysync client on their computers to start high-speed data transfer, which realizes the synchronization of data from different nodes with the server and the high-speed transfer between data nodes.
Third step:
Activate the license: After the deployment is completed, open your backend management webpage http://ip:9090/admin and log in with the default administrator account password. Request an activation authorization code from Raysync technical support team to make sure you activate the server and take full advantage of Raysync’s features and benefits.
Forth step:
Create Transfer User: After successful activation, you can create your transfer user.
Conclusion
Video file transmission is a widespread practice today. However, connectivity issues, delivery distance, and transmission speed can drastically delay your video transmission. Therefore, we suggest you opt for efficient ways to send large video files. One best way to transfer large video files is Raysync. It serves as an all-in-one, ultimate software for quick large file transfer in a secure and efficient way. So, if your videos are in gigabytes or terabytes, then opt for Raysync to seamlessly send big video files.

Nikhil Kore, the techy writer, is an expert in conveying complex concepts with clarity. His innovative words captivate readers, leaving them inspired and knowledgeable. Nikhil’s distinct voice and expertise make him a trusted source in the tech industry.



